Nội dung
1.Introduction to Inventory Management
In today’s globalized and highly competitive economy, inventory management plays a crucial role in the success of any business, from small retail shops to large manufacturing corporations. Inventory is not just the products or materials stored for future use or sale but is also a core part of the supply chain. It reflects a company’s ability to meet customer demand, optimize costs, and ensure uninterrupted production.
Effective inventory management not only minimizes storage costs but also enhances market responsiveness. However, it comes with significant challenges, especially in the digital age, where businesses face constant fluctuations in demand, shorter delivery times, and ongoing competitive pressures.
2.The Importance of Inventory Management
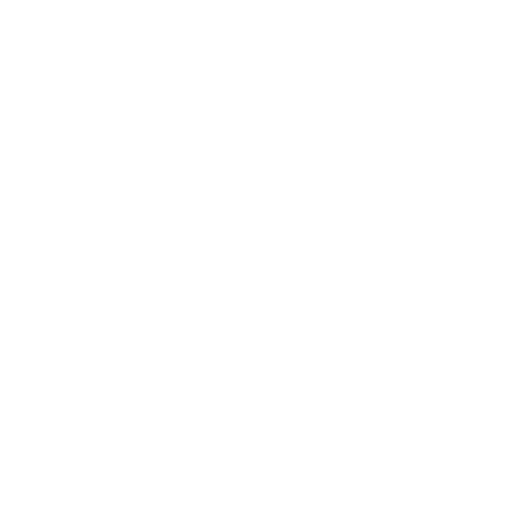
2.1 Ensuring Product Availability and Production Materials
One of the primary goals of inventory management is to ensure that a business always has enough products and materials to meet customer demand without causing disruptions to production or sales. A shortage of goods can lead to missed business opportunities, reduced customer satisfaction, and a damaged business reputation. On the other hand, excessive stockpiling can increase storage costs and result in wasted resources.
2.2 Cost Optimization
Effective inventory management helps businesses minimize storage-related costs, including warehouse rental, insurance, and management expenses. Tight control of inventory also reduces the costs associated with damage, loss, and unnecessary stock. By optimizing the inventory management process, companies can improve cash flow and maximize profits.
2.3 Meeting Market Demand
The ability to meet customer demand quickly and accurately is a key factor in staying competitive in today’s business environment. Efficient inventory management enables businesses to maintain flexibility in adjusting stock levels based on market fluctuations, thereby responding to customer needs swiftly and efficiently.
2.4 Reducing Risks
An efficient inventory management system helps companies reduce risks related to shortages or excess stock. This is particularly important in volatile industries like fashion, food, or technology, where careful inventory management can mitigate risks related to product spoilage, expiration, or obsolescence.
3.Challenges in Inventory Management
3.1 Demand Fluctuations
Customer demand is often unstable and can quickly change due to market trends, seasons, or economic factors. This presents a major challenge for forecasting and managing inventory. Inaccurate demand predictions can lead to shortages or excess inventory, resulting in lost revenue or increased storage costs.
3.2 Multi-Warehouse Management
For businesses with complex distribution systems or multiple warehouses, inventory management becomes more complicated. This requires a robust and accurate tracking system to ensure that goods are stored and distributed at the right time and in the right place.
3.3 Supply Chain Optimization
Supply chains are becoming increasingly complex, involving multiple suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers. This creates significant challenges in inventory management, especially when there are changes in the supply chain, such as supply disruptions, price fluctuations, or shifts in customer demand.
3.4 Cost – Reduction Pressure
In a competitive business environment, companies are constantly under pressure to reduce costs to maintain or improve profitability. This requires inventory management to be optimized to minimize storage and transportation costs without compromising service quality or the ability to meet customer demand.
4.Effective Inventory Management Methods
4.1 Just-in-Time (JIT) Method
Just-in-Time is an inventory management strategy where goods and materials are only ordered and produced when there is a specific demand. This method helps minimize inventory, reduce storage costs, and increase production efficiency. However, JIT requires a strong supply chain and close coordination between stakeholders to ensure materials and goods are always available when needed.
4.2 ABC Analysis
ABC analysis is a method of classifying inventory based on value and usage frequency. Inventory is divided into three categories:
- Category A: High-value items with low usage frequency. Close management of this group helps optimize capital usage.
- Category B: Items with moderate value and usage frequency. Good control is necessary to avoid shortages or excess.
- Category C: Low-value items with high usage frequency. Sufficient stock must be maintained to meet frequent demand.
4.3 First In, First Out (FIFO) Method
FIFO is an inventory management method where goods that are received first are also sold or used first. This method is particularly effective for industries with perishable products, such as food and pharmaceuticals, as it helps minimize the risk of spoilage or product obsolescence.
4.4 Leveraging Technology in Inventory Management
Technological advancements have brought powerful tools that help optimize inventory management. Modern inventory management software not only tracks inventory quantities accurately but also provides analytical reports, demand forecasting, and decision support. Technologies such as RFID, barcodes, IoT, and big data analytics are widely used to enhance inventory management efficiency.
4.5 Inventory Management Software
The adoption of inventory management software has led to significant improvements for businesses, centralizing data and enabling easy access. The integration of advanced technologies and modern calculation methods makes inventory management software an increasingly preferred choice for businesses.
The Smart Factory system developed by IVS is now available on a cloud platform, offering intelligent production and inventory management while saving costs, suitable for all businesses.
5.Results Achieved from Effective Inventory Management
Effective inventory management brings numerous key benefits to businesses. First, it helps optimize working capital by reducing unnecessary inventory and increasing capital utilization. Second, good inventory management allows businesses to respond to customer demand quickly and accurately, improving customer satisfaction and boosting brand reputation.
Moreover, efficient inventory management helps reduce risks related to product damage, obsolescence, or loss, which is especially critical for industries with high quality and safety standards, such as food, pharmaceuticals, or technology.
Finally, effective inventory management enhances the overall efficiency of the supply chain, helps businesses compete more effectively in the market, and manage





